Page 15 - Volume 8, Issue 4 - Winter 2012
P. 15
amplitudes, as they only occur after inertial cavitation has occurred. Preclinically, HIFU sonothrombolysis has been demonstrated in animal femoral models using an acoustic power of 300 W42,43 and in an embolic middle cerebral artery (MCA) model
44
Due to the high pressures and relatively high frequencies required for safe sonothrombolysis, studies conducted thus far have required a surgical cran- iotomy, however numerical simula- tions have shown that the application of this technique transcranially is fea- sible,46 though it may require the development of new multi-element phased arrays consisting of an order of magnitude more elements and the corresponding high power multi-ele-
ment driving technology.
Summary
Transcranial focused ultrasound is an emerging non-invasive treatment modality with many potential applica- tions. Ultrasound is unique in that it has the capability to initiate either
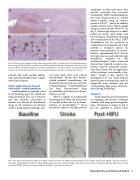
In Fig. 5, fluoroscopy images of a rabbit model pre-stroke, post-stroke, and post-treatment demonstrate blocking and recanalization of the MCA. HIFU thrombolysis has the potential to enable faster recanalization and it may provide a treatment option for patients contraindicated to throm-
45
using an acoustic power of 450 W.
bolytics—approximately 97%.
Fig. 4. Neural stem cells, tagged with green fluorescent protein (GFP), were delivered to the left hippocampus of the rat using focused ultrasound. A) Post-mortem GFP-immunohistochemistry confirms that stem cells are only present in the left (targeted) hemisphere. B) At 40x, the GFP-positive cells clearly exhibit a neuronal phenotype (arrows). C) No cells were detected in the non-sonicated hemisphere. Scale bars: A=500 mm, B,C=50 mm32
research with many possible applica- tions and the potential to have a signif- icant clinical impact.
Future applications of focused ultrasound—sonothrombolysis
Sonothrombolysis generally refers to the breaking apart of a blood clot using ultrasound. The use of transcra- nial low intensity ultrasound to enhance the efficacy of thrombolytic drugs in the treatment of ischemic stroke is being explored through clini-
cal trials, both with36 and without microbubbles. Results have demon- strated enhanced recanalization, but have also been met with increased risks
37,38
39
breaking apart a blood clot in less than 30 seconds without the use of throm-
Sonothrombolysis has been demonstrated using microbubbles in the absence of throm-
of hemorrhaging.
bolytics, as well.
HIFU is capable of mechanically
40,41 procedures require very high pressure
bolytics or microbubbles.
These
Fig. 5. Two-dimensional projection images of the rabbit cerebral vasculature are displayed. Normal perfusion of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) is observed in the base-
line images. The blockage of the MCA is confirmed following injection of an embolism through a 20g catheter in the internal carotid artery. Following high intensity focused
ultrasound (HIFU) treatment, restoration of flow in the MCA is demonstrated (red arrow).
44
Transcranial Focused Ultrasound Surgery 11